Tính diện tích hình phẳng giới hạn bởi:
LG a
Đồ thị hai hàm số \(y = {x^2} + 1\) và \(y = 3 – x\).
Phương pháp giải:
Tính diện tích hình phẳng giới hạn bởi các đồ thị hàm số \(y = f\left( x \right),y = g\left( x \right),\) \(x = a,x = b\).
+) B1: Tìm nghiệm \(a \le {x_1} < {x_2} < ... < {x_n} \le b\) của phương trình hoành độ giao điểm \(f\left( x \right) = g\left( x \right)\).
+) B2: Tính diện tích theo công thức:
\(S = \int\limits_a^b {\left| {f\left( x \right) - g\left( x \right)} \right|dx} \)
\( = \int\limits_a^{{x_1}} {\left| {f\left( x \right) - g\left( x \right)} \right|dx} \) \( + \int\limits_{{x_1}}^{{x_2}} {\left| {f\left( x \right) - g\left( x \right)} \right|dx} \) \( + ... + \int\limits_{{x_{n - 1}}}^{{x_n}} {\left| {f\left( x \right) - g\left( x \right)} \right|dx} \) \( + \int\limits_{{x_n}}^b {\left| {f\left( x \right) - g\left( x \right)} \right|dx} \)
\( = \left| {\int\limits_a^{{x_1}} {\left[ {f\left( x \right) - g\left( x \right)} \right]dx} } \right|\)\( + \left| {\int\limits_{{x_1}}^{{x_2}} {\left[ {f\left( x \right) - g\left( x \right)} \right]dx} } \right|\) \( + ... + \left| {\int\limits_{{x_{n - 1}}}^{{x_n}} {\left[ {f\left( x \right) - g\left( x \right)} \right]dx} } \right|\) \( + \left| {\int\limits_{{x_n}}^b {\left[ {f\left( x \right) - g\left( x \right)} \right]dx} } \right|\)
Lời giải chi tiết:
Cách 1:
Phương trình hoành độ giao điểm của hai đồ thị là:
\({x^2} + 1 = 3 - x \) \(\Leftrightarrow {x^2} + x - 2 = 0 \Leftrightarrow \left[ \matrix{
x = 1 \hfill \cr
x = - 2 \hfill \cr} \right.\)
\(S = \int\limits_{ - 2}^1 {\left| {{x^2} + x - 2} \right|} dx\) \( = \left| {\int\limits_{ - 2}^1 {\left( {{x^2} + x - 2} \right)dx} } \right|\) \( = \left| {\left. {\left( {\dfrac{{{x^3}}}{3} + \dfrac{{{x^2}}}{2} - 2x} \right)} \right|_{ - 2}^1} \right|\) \( = \left| { - \dfrac{7}{6} - \dfrac{{10}}{3}} \right| = \dfrac{9}{2}\)
Cách khác:
Phương trình hoành độ giao điểm của hai đồ thị là:
\({x^2} + 1 = 3 - x \) \(\Leftrightarrow {x^2} + x - 2 = 0 \Leftrightarrow \left[ \matrix{
x = 1 \hfill \cr
x = - 2 \hfill \cr} \right.\)
Với mọi \(x \in \left[ { - 2;1} \right]\) thì \({x^2} + x - 2 \le 0\). Khi đó, \(\left| {{x^2} + x - 2} \right| = - {x^2} - x + 2\)
Diện tích cần tìm là:
\(S = \int\limits_{ - 2}^1 {\left| {{x^2} + x - 2} \right|} dx\) \( = \int\limits_{ - 2}^1 {\left( { - {x^2} - x + 2} \right)dx} \) \( = \left. {\left( { - \dfrac{{{x^3}}}{3} - \dfrac{{{x^2}}}{2} + 2x} \right)} \right|_{ - 2}^1\) \( = \dfrac{7}{6} - \left( { - \dfrac{{10}}{3}} \right) = \dfrac{9}{2}\)
LG b
Các đường có phương trình \(x = {y^3}\), \(y = 1\), và \(x = 8\).
Phương pháp giải:
Sử dụng công thức \(S = \int\limits_a^b {\left| {f\left( x \right) - g\left( x \right)} \right|dx} \)
Lời giải chi tiết:
Ta có: \(x = {y^3} \Rightarrow y = {x^{\frac{1}{3}}}\)
Diện tích cần tìm là:
\(S = \int\limits_1^8 {({x^{{1 \over 3}}} - 1)dx = \left. {\left( {{3 \over 4}{x^{{4 \over 3}}} - x} \right)} \right|_1^8} \) \(= {{17} \over 4}\)
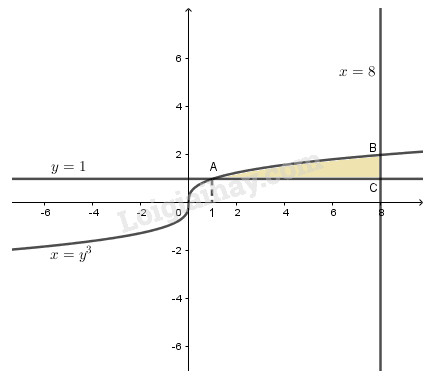
Cách khác:
Tung độ giao điểm của đường cong x=y3 và đường thẳng x = 8 là nghiệm của phương trình y3=8 <=> y = 2. Vậy diện tích cần tìm là:
\(S = \int\limits_1^2 {\left| {{y^3} - 8} \right|dy} \)\( = \left| {\int\limits_1^2 {\left( {{y^3} - 8} \right)dy} } \right|\) \( = \left| {\left. {\left( {\dfrac{{{y^4}}}{4} - 8y} \right)} \right|_1^2} \right|\) \( = \left| { - 12 - \left( { - \dfrac{{31}}{4}} \right)} \right|\)\( = \left| { - \dfrac{{17}}{4}} \right| = \dfrac{{17}}{4}\)
LG c
Đồ thị của hàm số \(y = \sqrt x ,y = 6 - x\) và trục hoành.
Lời giải chi tiết:
Phương trình hoành độ giao điểm của 2 đồ thị là:
\(\eqalign{
& \sqrt x = 6 - x \Leftrightarrow x + \sqrt x - 6 = 0 \cr
& \Leftrightarrow \sqrt x = 2 \Leftrightarrow x = 4 \cr} \)
\(S = {S_{OAB}} + {S_{ABC}}\)
\( = \int\limits_0^4 {\sqrt x dx} + \dfrac{1}{2}.AB.AC\)\( = \int\limits_0^4 {{x^{\dfrac{1}{2}}}dx} + \dfrac{1}{2}.2.2 = \left. {\dfrac{2}{3}{x^{\dfrac{3}{2}}}} \right|_0^4 + 2\) \( = \dfrac{2}{3}.8 + 2 = \dfrac{{22}}{3}\)
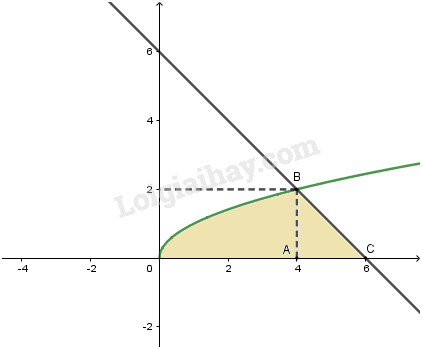
Cách khác:
Ta có: y=√x <=> y2=x (y ≥ 0);y=6-x <=> x = 6 – y
Tung độ giao điểm của hai đường thẳng x=y2;x=6-y là nghiệm của phương trình
\({y^2} = 6 - y\) \( \Leftrightarrow {y^2} + y - 6 = 0\) \( \Leftrightarrow \left[ \begin{array}{l}y = - 3\left( {loai} \right)\\y = 2\end{array} \right.\)
Vậy diện tích cần tìm:
\(S = \int\limits_0^2 {\left| {{y^2} - \left( {6 - y} \right)} \right|dy} \) \( = \left| {\int\limits_0^2 {\left( {{y^2} + y - 6} \right)dy} } \right|\) \( = \left| {\left. {\left( {\dfrac{{{y^3}}}{3} + \dfrac{{{y^2}}}{2} - 6y} \right)} \right|_0^2} \right|\) \( = \left| { - \dfrac{{22}}{3} - 0} \right| = \dfrac{{22}}{3}\)

