Before
Before You Read
Work in pairs. Look at the pictures and answer the questions that follow.
(Làm việc từng đôi. Nhìn vào các hình và trả lời câu hỏi kèm theo.)
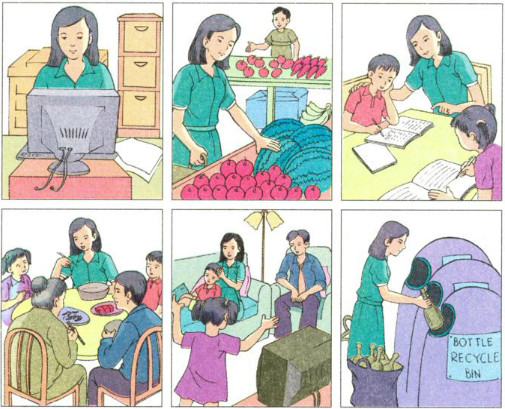
1. How many roles does this woman have?
(Phụ nữ này đóng bao nhiêu vai trò?)
2. Is her life typical of a Vietnamese woman's life? Why/Why not?
(Có phải cuộc sống của bà là cuộc sống của người phụ nữ Việt Nam? Tại sao/ tại sao không?)
Lời giải chi tiết:
1. This woman has two roles: a wife's role and a mother's role.
(Người phụ nữ này có hai vai trò: vai trò của người vợ và vai trò của một người mẹ.)
2. Yes, it is, because it's the Vietnamese traditional lifestyle and culture.
(Đúng, đó là vì lối sống và văn hoá truyền thống của Việt Nam.)
While
While You Read
Read the text and do the tasks that follow.
(Đọc đoạn văn và làm bài tập kèm theo.)
Throughout much of the history of human civilization, deep-seated cultural beliefs allowed women only limited roles in society. Many people believed that women’s natural roles were as mothers and wives. These people considered women to be better suited for childbearing and homemaking rather than for involvement in the public life of business or politics. Widespread doubt about women’s intellectual ability led most societies to deny education, employment and many legal and political rights to women. It was men who controlled most positions of employment and power in society.
The struggle for women’s rights - the rights that establish the same social, economic, and political status for women as for men - began in the 18th century during a period known as the Age of Enlightenment. During this period, political philosophers in Europe began to argue that all individuals, male or female, were born with natural rights that made them free and equal. These pioneer thinkers advocated that women should not be discriminated against on the basis of their sex.
Today, although their status varies in different countries, women in most parts of the world have gained significant legal rights. The most important of these are: the right to have equal work opportunities and pay to men, the right to vote, and the right to formal education.
Phương pháp giải:
Dịch bài đọc:
Trải qua chiều dài lịch sử của nền văn minh nhân loại, những niềm tin văn hóa lâu đời cho phép phụ nữ chỉ có những vai trò hạn chế nhất định trong xã hội. Nhiều người tin rằng vai trò tự nhiên của phụ nữ là mẹ và vợ. Những người này xem phụ nữ phù hợp cho việc sinh con và việc chăm sóc gia đình hơn là dấn thân vào đời sống xã hội của việc kinh doanh hay chính trị. Sự nghi ngờ phổ biến về khả năng trí thức của phụ nữ đã đưa nhiều xã hội từ chối việc giáo dục, việc làm và nhiều quyền pháp lí và chính trị đối với phụ nữ. Chính phụ nữ là người kiểm soát phần lớn việc làm và quyền lực trong xã hội.
Cuộc tranh đấu cho quyền của phụ nữ- những quyền thiết lập cùng một địa vị xã hội. văn hóa và chính trị cho phụ nữ cũng như đàn ông - bắt đầu vào thế kỉ 18, trong suốt thời kì được biết như là Thời đại Ánh Sáng. Trong suối thời kì này, các nhà triết học chính trị ở Âu châu bắt đầu lí giải rằng tất cả cá nhân, nam hay nữ, được sinh ra với quyền tự nhiên làm cho họ tự do và bình đẳng. Những nhà tư tưởng tiên phong này biện hộ rằng phụ nữ không nên bị phân biệt đối xử vì căn cứ vào nền tảng giới tính của họ.
Ngày nay, dù địa vị của họ thay đổi ở nhiều quốc gia khác nhau, phụ nữ phần lớn trên thế giới đã đạt nhiều quyền pháp lí quan trọng. Quyền quan trọng nhất trong những quyển này là: quyền có việc làm và trả lương như đàn ông, quyền bầu cử và quyền có nền giáo dục chính quy.
Task 1
Task 1: Give the Vietnamese equivalents to the following words and phrases.
(Cho từ tiếng Việt tương đương với những từ và cụm từ sau.)
1. human civilization: ___________
2. childbearing: ___________
3. involvement: ___________
4. Age of Enlightenment: ___________
5. deep-seated cultural beliefs: ___________
6. homemaking: ___________
7. intelleclual ability: ___________
8. equal work opportunity: ___________
Lời giải chi tiết:
1. human civilization - nền văn minh nhân loại
2. childbearing - việc sinh con
3. involvement - tự dấn thân, tham gia
4. Age of Enlightenment - Thời đại ánh sáng
5. deep-seated cultural beliefs - những niềm tin văn hóa lâu đời
6. homemaking - việc chăm sóc gia đình
7. intelleclual ability - khả năng trí thức/hiểu biết
8. equal work opportunity - cơ hội nghề nghiệp/ việc làm bình đẳng
Task 2
Task 2: Choose the best option A, B, C or D to answer the following questions.
(Chọn câu trả lời đúng nhất A, B,C hay D đề trả lời những câu hỏi sau.)
1. According to the text, what was the main role traditionally accorded to women?
A. working in education
B. building houses
C. taking care of the house and family
D. working in factories
2. Before the 18th century, what was the attitude of societies towards women’s intellectual ability?
A. respectful
B. supportive
C. resentful
D. disbelieving
3. According to the text, what is the purpose of the struggle for women’s rights?
A. to free women from housework
B. to establish a friendly relationship between men and women
C. to bring equality between men and women
D. to argue that women have better intellectual ability
4. What do “these pioneer thinkers’” at the end of paragraph 2 refer to?
A. 18th century European people
B. 18th century European political philosophers
C. 18th century European women
D. 18th century European politicians
5. Which of the following is NOT mentioned in the last paragraph as one of women’s legal rights today?
A. the right to hold property
B. the right to equal pay
C. equal employment opportunity rights
D. the right to vote
Lời giải chi tiết:
| 1. C | 2. D | 3. C | 4. B | 5. A |
1. Theo văn bản, theo truyền thống vai trò chính phù hợp với phụ nữ là gì?
A. làm việc trong lĩnh vực giáo dục
B. xây nhà
C. chăm sóc ngôi nhà và gia đình
D. làm việc trong nhà máy
Thông tin: (đoạn 1) “Many people believed that women’s natural roles were as mothers and wives. These people considered women to be better suited for childbearing and homemaking”
2. Trước thế kỷ 18, Thái độ của xã hội đối với khả năng trí tuệ của phụ nữ là gì?
A. tôn trọng
B. ủng hộ
C. phản ứng
D. không tin tưởng
Thông tin: (đoạn 1) “Widespread doubt about women’s intellectual ability led most societies to deny education, employment and many legal and political rights to women.”
3. Theo văn bản, mục đích của cuộc đấu tranh giành quyền phụ nữ là gì?
A. để giải phóng phụ nữ ra khỏi nhà
B. thiết lập một mối quan hệ thân thiện giữa nam và nữ
C. mang lại sự bình đẳng giữa nam và nữ
D. để cho rằng phụ nữ có khả năng trí tuệ tốt hơn.
Thông tin: (đoạn 2) “The struggle for women’s rights - the rights that establish the same social, economic, and political status for women as for men”
4. Những "nhà tư tưởng tiên phong" này thay thế cho cái gì ở cuối đoạn 2?
A. Người Châu Âu thế kỷ 18
B. Các triết gia chính trị châu Âu trong thế kỷ 18
C. Phụ nữ châu Âu thế kỷ 18
D. Các chính trị gia châu Âu Thế kỷ 18
Thông tin: (đoạn 2) “... political philosophers in Europe began to argue that all individuals, male or female, were born with natural rights that made them free and equal. These pioneer thinkers advocated that”
5. Những điều sau đây KHÔNG được đề cập đến ở đoạn cuối như là một trong các quyền hợp pháp của phụ nữ ngày nay?
A. quyền giữ tài sản
B. quyền được trả lương bình đẳng
C. quyền cơ hội việc làm bình đẳng
D. quyền bầu cử
Thông tin: “The most important of these are: the right to have equal work opportunities and pay to men, the right to vote, and the right to formal education.”
Task 3
Task 3: Choose the best title for the passage.
(Chọn tựa đề đúng nhất cho đoạn văn.)
A. Intellectual Ability (Khả năng Trí tuệ)
B. The Age of Enlightenment (Thời kỳ khai sáng)
C. Women’s Rights (Quyền của phụ nữ)
D. Women’s Role in Education (Vai trò của phụ nữ trong giáo dục)
Lời giải chi tiết:
C. Women’s Rights (Quyền của phụ nữ)
After
After You Read
Work in pairs. Summarize the reading passage by writing ONE, sentence for each paragraph.
(Làm việc từng đôi. Tóm tắt đoạn văn đọc bằng cách viết một câu cho mỗi đoạn văn.)
Lời giải chi tiết:
- Paragraph ONE: In the past, women were limited to natural roles: mother's and wife’s because of widespread doubt about their intellectual ability.
(Đoạn 1: Trong quá khứ, phụ nữ bị giới hạn trong vai trò thuộc về bản chất tự nhiên: là làm vợ và mẹ vì bị nghi ngờ về khả năng trí tuệ.)
- Paragraph TWO: The struggle for women's rights began in the 18th century with European philosophers’ thoughts that women should not be discriminated on the basis of sex.
(Đoạn 2: Cuộc đấu tranh cho quyền của phụ nữ bắt đầu vào thế kỷ 18 với tư tưởng của các triết gia châu Âu rằng phụ nữ không nên bị phân biệt đối xử dựa trên giới tính.)
- Paragraph THREE: Women now enjoy significant legal rights such as equal work and pay rights, the right to vote and to get a formal education.
(Đoạn 3: Phụ nữ bây giờ được hưởng các quyền pháp lý quan trọng như công việc và quyền trả lương bình đẳng, quyền bầu cử và để có được nền giáo dục chính thức.)

